Last Updated:07 5月. 2014
Fetal tachyarrhythmia
What is fetal tachyarrhythmia?+ SHOW
Cases in which the fetal heart rate is continually 180 bpm or higher may be defined as fetal tachyarrhythmia. In some cases it disappeared naturally, however; it can develop fetal edema (where water builds up in the chest or abdomen, and the whole body swells) when it continues for longer time. Fetal edema can be a cause of intrauterine fetal death or newborn mortality. Recent reports have shown the effectiveness of fetal therapy for the fetal tachyarrhythmia; however, the treatment method has not been fully established. Some clinical trials are undergoing in Japan in order to confirm its effectiveness and safety.
What is the cause of fetal tachyarrhythmia?+ SHOW
Fetal tachyarrhythmia occurs as a result of the pathological change of the passage of electrostimulation. Although fetal tachyarrhythmia occurs in many forms, supraventricular tachycardia or atrial flutter are found in most cases. (see Fig.)
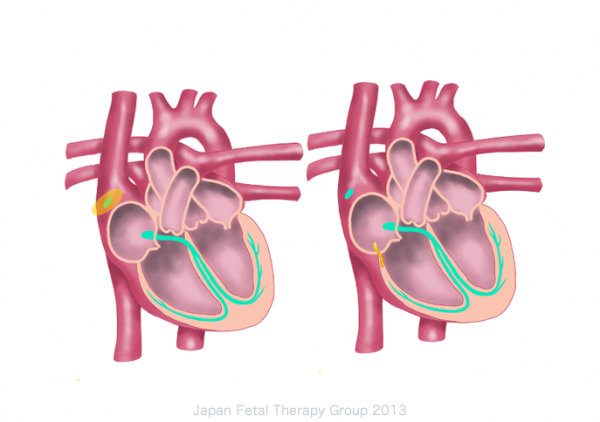
Left: Normal Right: supraventricular tachycardia (reentry)
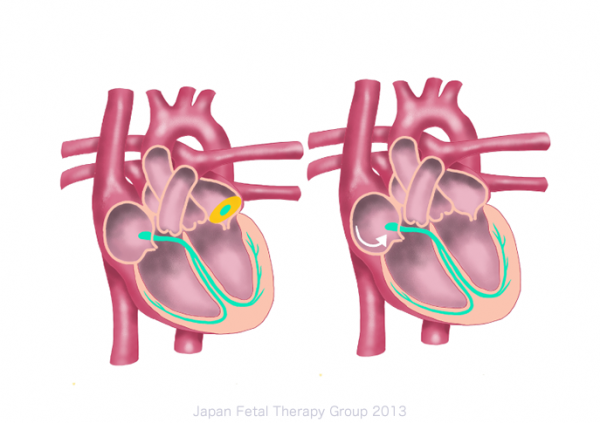
Left: atrial tachycardia (increased automaticity) Right: atrial flutter (micro-reentry)
How is it diagnosed?+ SHOW
Fetal tachyarrhythmia is diagnosed via an ultrasound examination. It is classified by the frequency of the atrial contraction, the ventricular contraction or the rate of them. It is also classified by the timing of the initiation of the atrial and ventricular contraction into atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia or other types of fetal tachyarrhythmia. If it is supraventricular tachycardia, the detail sub-classification is provided.
What is the usual method of management?+ SHOW
Fetal tachyarrhythmia can be disappeared naturally, but when it continues, early termination of the pregnancy and the treatment to the newborn might be required. After birth, in order to stop the arrhythmia a medication, and a defibrillator is used to the newborn. However, the earlier termination of the pregnancy can be a cause of the disadvantage in prematurity of the newborn.
What is fetal therapy?+ SHOW
Fetal therapy involves administering antiarrhythmic agents to the fetus in utero via mother. If arrhythmia is stopped, the pregnancy can be continued, allowing the infant to be delivered in the better condition. Because of the medication to the healthy mother who doesn’t need to be treated herself, the intensive observation should be done to avoid the serious side effects of the drugs.
What are the results and prognosis of this treatment?+ SHOW
Some reports have shown that around 80% of the cases of fetal tachyarrhythmia found to be controlled, resulting the reduction of the premature delivery and the cesarean section rate. A pilot study which was done before in Japan has shown the same results.
References+ SHOW
1.Ulrich Gembruch ”fetal tachyarrythmia” Fetal Cardiology Embryology, genetics, Physioloosy, Echocardiographic Evaluation, Diagnosis and Perinatal Management od Cardiac Disease. Yagel et.al. London New York Taylar and Francis 2005
2.M Krapp, T Kohl, JM Simpson, Review of diagnosis, treatment and outcome of fetal atrial flutter compared with supraventricular tachycardia Heart 2003: 89; 913-917
3.Fouron JC, Fournier A, Lamarche J et.al. Management of fetal tachycarrhythmia based on superior vena cava/aorta Doppler flow recordings. Heart 2003: 89; 1211-6


